Marine Animals Definition Biology

An animal belonging to the mammalian order Sirenia which includes manatees and dugongs.
Marine animals definition biology. What is Marine Biology. Marine biology is the study of marine ecosystems marine organisms and human interactions with these environments and species. A marine biologist is someone who is interested in learning and studying marine organisms and what their lives are like in their natural habitats.
Spongin- flexible protein fibers. Marine environments are therefore the most common habitat on Earth. As a marine biologist you may study a wide range of topics from the behavior physiology and ecology of specific groups of organisms to the interactions between human activity and aquatic environments.
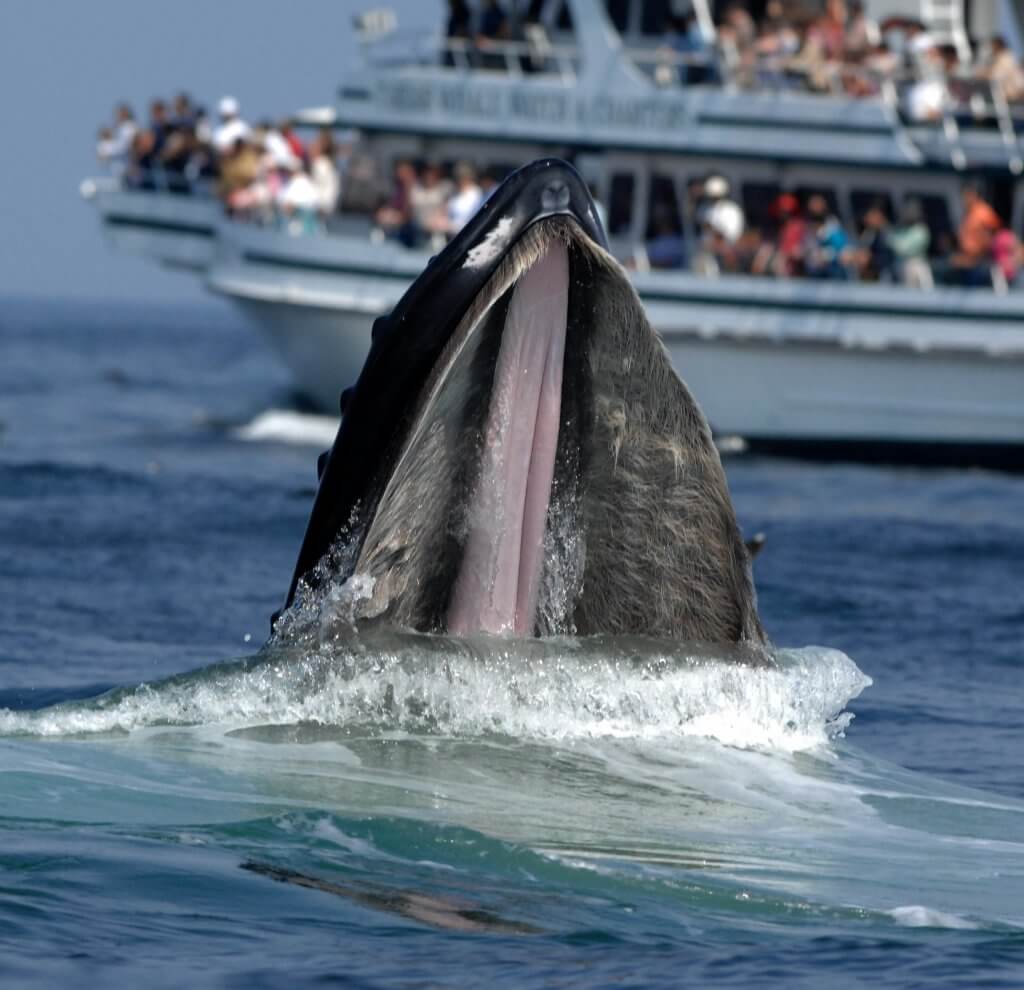
When many people think about a marine biologist they picture a dolphin trainer. Collar cells- create moving force in a sponges body. Marine biology is the study of marine organisms their behaviors and interactions with the environment.
Marine biologists study biological oceanography and the associated fields of chemical physical and geological oceanography to understand marine organisms. Our ocean coasts and estuaries are home to diverse living things. Marine biologists study a wide variety of aquatic organisms from microscopic plankton to massive whales.
It is the largest and most diverse biome in the world. Given that in biology many phyla families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. The study of this biome and its components is known as marine biology while the scientists who study marine life are known as marine biologists.
Osculum- large opening that lets water out. There are a vast array of career choices one can pick from - from studying large ocean animals and what they eat to. The study of marine life is called marine biology and a person that studies marine life is called a marine biologist.